Spark plug
A spark plug is used as a source of ignition, as the "spark" in its name might imply. It is a key component of internal combustion engines and its primary function is to ignite a fuel/air mixture within the combustion chamber of a car, or other system. Figure 1 shows plugs, the spark travels across the gap on the left side of the spark plug.
The voltage in the ignition system must be high enough to create a spark across the spark plug gap (see figure 2), much like a bolt of lightning traveling from the clouds to the Earth. These voltages can be anywhere from 40 kV to 100 kV, in other words high voltage.[2]
Spark plugs are an important part of gasoline engines, but not a part of diesel engines, since diesel is ignited by the compression of the gas instead.
To learn more about spark plugs, click here.
References
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/10/Spark_plugs.jpg
- ↑ HowStuffWorks, Spark Plug [Online], Available: http://auto.howstuffworks.com/ignition-system2.htm
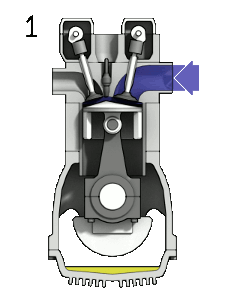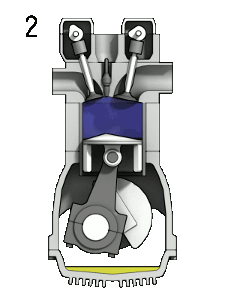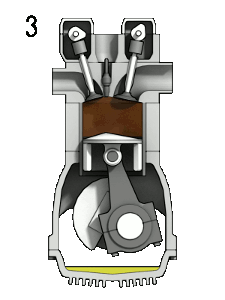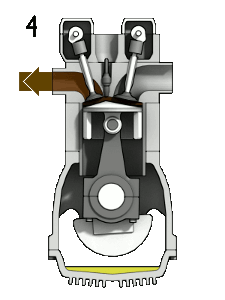
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/dc/4StrokeEngine_Ortho_3D_Small.gif


