Catchment
A catchment, or drainage basin, is defined as an area that collects precipitation and drains it into a network of water channels. This network often drains into a larger outlet, such as a river, reservoir, or body of water. Catchments are usually open systems and precipitation and other materials flow freely into and out of the system.[1]
The surface topography of an area determines the size of a catchment area. A catchment area is bound by raised natural features, such as hills or mountains, off of which precipitation flows into a drainage network in an area of depression. Large catchments can be composed of smaller sub-catchments. Sub-catchments feed tributaries, which are small streams that feed larger streams or rivers.[2]
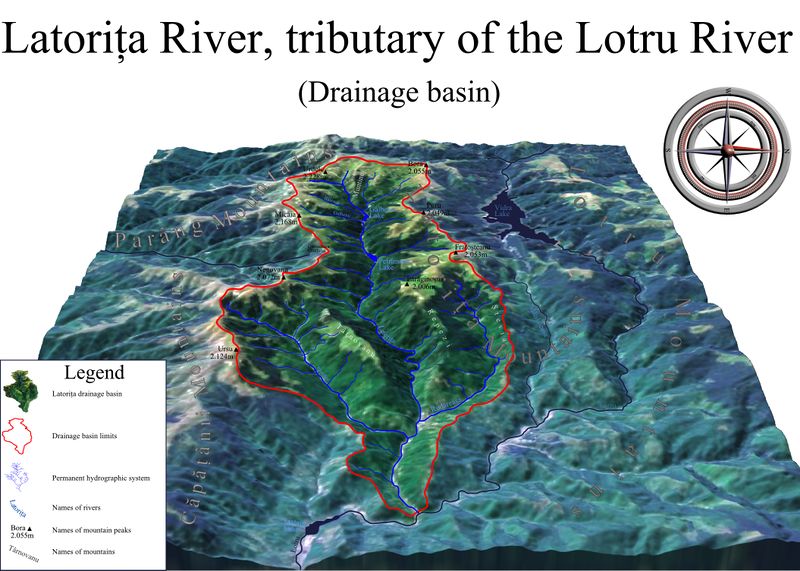
Figure 1. A diagram of a catchment area, or drainage basin, of the Latorița River in Romania.[3]
References
- ↑ Wagener, T., Sivapalan, M., Troch, P., & Woods, R. "Catchment Classification and Hydrologic Similarity," Geography Compass, vol. 1, p. 2, 2007. [Online]. Available: http://water.engr.psu.edu/wagener/PublicationsPDFs/GeographyCompass2007%20Wagener%20et%20al.pdf. [Accessed: 07-Mar-2018 ].
- ↑ Waikato Regional Council, New Zealand Government. "Understanding Your Catchment". [Online]. Available: https://www.waikatoregion.govt.nz/assets/PageFiles/5949/04understanding.pdf. [Accessed: 07-Mar-2018 ].
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:EN_Bazinul_hidrografic_al_Raului_Latorita,_Romania.jpg Accessed March 16th, 2018.

