Crankshaft: Difference between revisions
J.williams (talk | contribs) m (1 revision imported) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Done | [[Category:Done 2018-07-20]] | ||
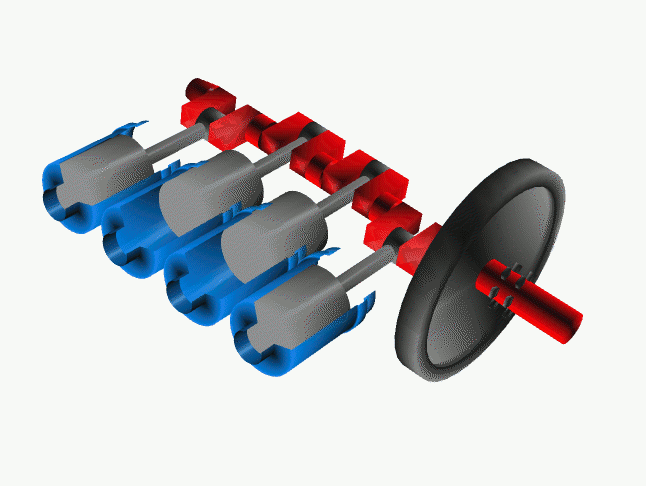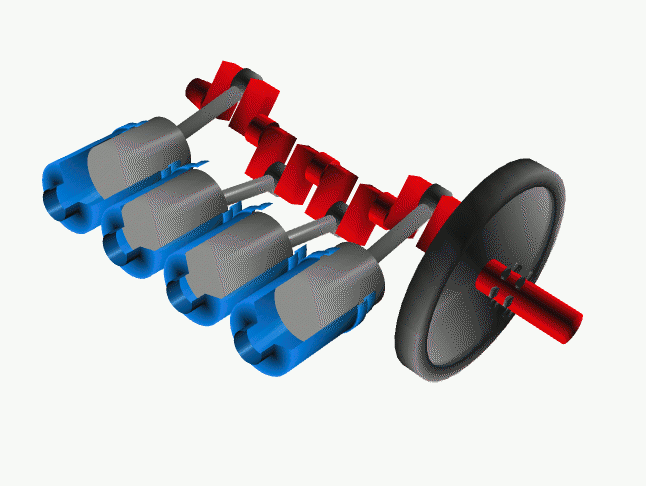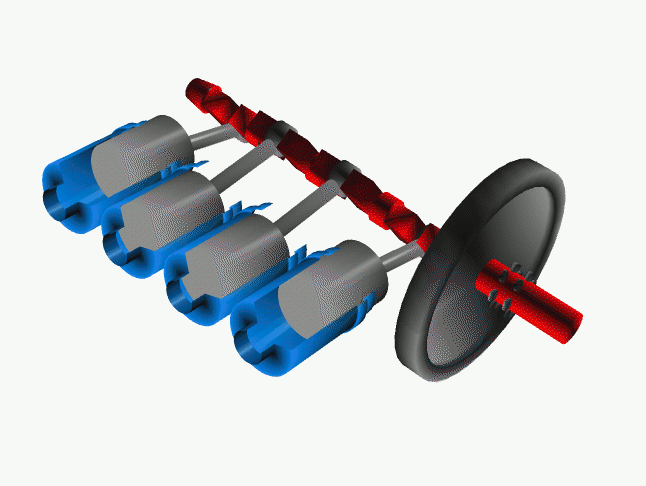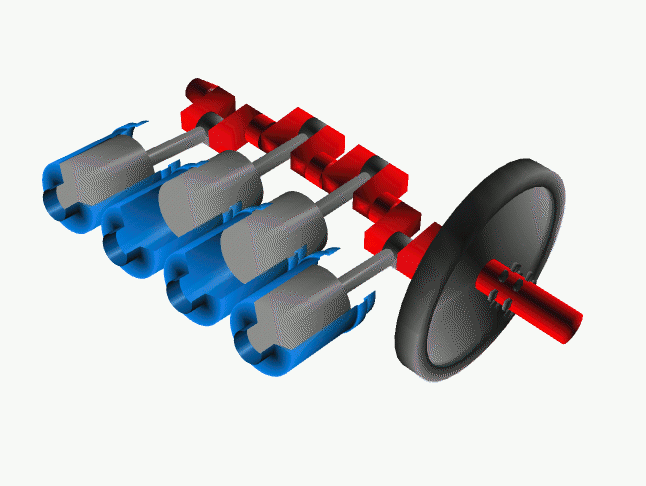
<onlyinclude>A '''crankshaft''' is a part in a [[reciprocating engine]] | <onlyinclude>A '''crankshaft''' is a part in a [[reciprocating engine]] that rotates due to the reciprocating motion of the pistons. However in a pump, the crankshaft's motion causes the piston to move back and forth.</onlyinclude><ref>A. Atkins and M. Escudier, A dictionary of mechanical engineering</ref> The crankshaft is connected to the pistons by "crankpins" which have an offset axis allowing this conversion of motion to be accomplished, and can be viewed in Figure 1. Since the common four-stroke cycle (Figure 2) of the reciprocating engine isn't continuous, the crankshaft is often connected to a flywheel which is used to store [[rotational energy]] in order to reduce the pulsation or choppiness of the pistons. | ||
<gallery | <gallery caption="Crankshaft and Pistons" mode=packed heights=350px> | ||
File:Cshaft.gif|Figure 1: The crankshaft (red) converts reciprocating motion from the pistons (grey) which is often combined with a flywheel (black).<ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ac/Cshaft.gif</ref> | File:Cshaft.gif|Figure 1: The crankshaft (red) converts reciprocating motion from the pistons (grey) which is often combined with a flywheel (black).<ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ac/Cshaft.gif</ref> | ||
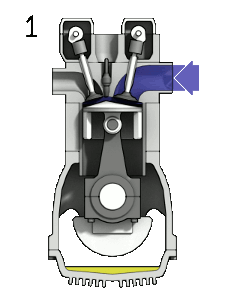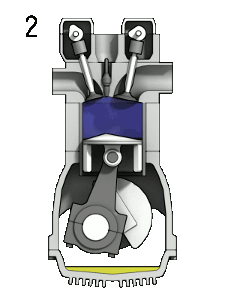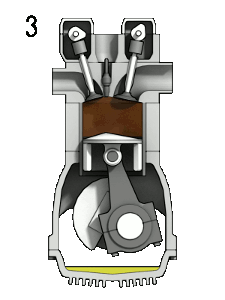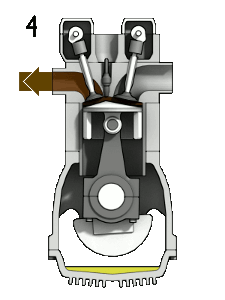
File:4StrokeEngine.gif|Figure 2: 4-stroke internal combustion engine. 1:fuel injection, 2:ignition, 3:expansion(work is done), 4:exhaust.<ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internal_combustion_engine#mediaviewer/File:4StrokeEngine_Ortho_3D_Small.gif</ref> | File:4StrokeEngine.gif|Figure 2: 4-stroke internal combustion engine. 1:fuel injection, 2:ignition, 3:expansion(work is done), 4:exhaust.<ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internal_combustion_engine#mediaviewer/File:4StrokeEngine_Ortho_3D_Small.gif</ref> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==For Further Reading== | |||
*[[Reciprocating engine]] | |||
*[[Rotational energy]] | |||
*[[Flywheel]] | |||
*[[Piston]] | |||
*[[Heat engine]] | |||
*Or explore a [[Special:Random|random page]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
[[Category:Uploaded]] | [[Category:Uploaded]] | ||
Revision as of 17:05, 17 July 2018
A crankshaft is a part in a reciprocating engine that rotates due to the reciprocating motion of the pistons. However in a pump, the crankshaft's motion causes the piston to move back and forth.[1] The crankshaft is connected to the pistons by "crankpins" which have an offset axis allowing this conversion of motion to be accomplished, and can be viewed in Figure 1. Since the common four-stroke cycle (Figure 2) of the reciprocating engine isn't continuous, the crankshaft is often connected to a flywheel which is used to store rotational energy in order to reduce the pulsation or choppiness of the pistons.
- Crankshaft and Pistons
Figure 1: The crankshaft (red) converts reciprocating motion from the pistons (grey) which is often combined with a flywheel (black).[2]
Figure 2: 4-stroke internal combustion engine. 1:fuel injection, 2:ignition, 3:expansion(work is done), 4:exhaust.[3]
For Further Reading
References
- ↑ A. Atkins and M. Escudier, A dictionary of mechanical engineering
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ac/Cshaft.gif
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internal_combustion_engine#mediaviewer/File:4StrokeEngine_Ortho_3D_Small.gif