Nonane: Difference between revisions
J.williams (talk | contribs) m (1 revision imported) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Done 2015-06 | [[Category: Done 2015-09-06]] | ||
<onlyinclude>'''Nonane''' is a [[hydrocarbon]] that can be burned as a [[fuel]]. | <onlyinclude>'''Nonane''' is a [[hydrocarbon]] that can be burned as a [[fuel]]. Its [[chemical]] formula is C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>20</sub></onlyinclude>, and it is a [[volatile]], colourless [[liquid]] that has a gasoline-like odour. Nonane, like other straight-chained [[alkane|alkanes]], is not soluble in [[water]].<ref name=pubchem> National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2015). ''Properties of Nonane'' [Online]. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/nonane#section=Color [February 16,2015]. </ref> | ||
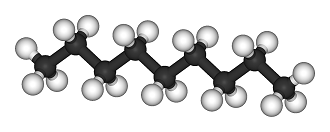
[[File:Nonane-3D-balls.png|500px|framed|center|Figure 1. Ball and stick model of heptane, the white is [[hydrogen]] and the black is [[carbon]].<ref> "Nonane-3D-balls". Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png#mediaviewer/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png </ref>]] | [[File:Nonane-3D-balls.png|500px|framed|center|Figure 1. Ball and stick model of heptane, the white is [[hydrogen]] and the black is [[carbon]].<ref> "Nonane-3D-balls". Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png#mediaviewer/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png </ref>]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| [[Molar mass]] || 128.26 [[kilogram|gram]]s/[[mole]] | | [[Molar mass]] || 128.26 [[kilogram|gram]]s/[[mole]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Melting | | [[Melting point]] || -51<sup>o</sup>C<ref name =elmhurst>Charles E. Ophardt. (2003). ''Virtual Chembook - Hydrocarbon Boiling Points'' [Online]. Available: http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/vchembook/501hcboilingpts.html [February 16,2015].</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Boiling | | [[Boiling point]] || 151<sup>o</sup>C<ref name =elmhurst/> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
[[Category:Uploaded]] | [[Category:Uploaded]] | ||
[[category:Ian edit]] | |||
Revision as of 19:23, 17 September 2015
Nonane is a hydrocarbon that can be burned as a fuel. Its chemical formula is C9H20, and it is a volatile, colourless liquid that has a gasoline-like odour. Nonane, like other straight-chained alkanes, is not soluble in water.[1]
Nonane is obtained from refining petroleum but it can also be produced adding hydrogen, , to nonene,
. This reaction is known as hydrogenation. Nonane is also a component in automotive and jet fuel. The second major use for nonane is as an ingredient in organic solvents. This is due to the fact that it is insoluble in water, as it makes it a good solvent for other hydrophobic molecules.[3]
Nonane undergoes hydrocarbon combustion, combining with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. The balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of nonane is:
Properties
Below is a table of some of the basic properties of nonane.
| Chemical formula | C9H20 |
| Molar mass | 128.26 grams/mole |
| Melting point | -51oC[4] |
| Boiling point | 151oC[4] |
References
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2015). Properties of Nonane [Online]. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/nonane#section=Color [February 16,2015].
- ↑ "Nonane-3D-balls". Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png#mediaviewer/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png
- ↑ Andrea Kropp. (2015). Nonane: Structure & Uses [Online]. Available: http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/nonane-structure-uses.html [February 16, 2015].
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Charles E. Ophardt. (2003). Virtual Chembook - Hydrocarbon Boiling Points [Online]. Available: http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/vchembook/501hcboilingpts.html [February 16,2015].