Electrical load
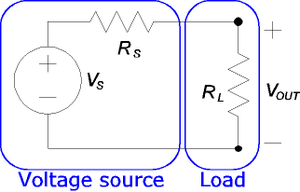
An electrical load is simply any component of a circuit that consumes power or energy. In a household setting, the most obvious examples of electrical loads include light bulbs and appliances. In a more general sense, any resistor or electric motor in a circuit that converts electrical energy into light, heat, or useful motion constitutes a load on the circuit. Simplified circuit diagrams usually show the load with the symbol for resistors (see Figure 1). [1]
The load of a circuit is inversely proportional to current flow as bigger loads lower the current in a circuit. However, if no significant load is present in a closed circuit, a short circuit will result and potentially cause significant damage.[2]
For Further Reading
For further information please see the related pages below:
- Electric circuit
- Light bulb
- Battery
- Capacitor
- Resistor
- Or explore a random page!
References
- ↑ Electrical Systems Training [Online]. Available: http://www.toolingu.com/class-550205-parallel-circuit-calculations-205.html
- ↑ What is a circuit? [Online]. Available: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/what-is-a-circuit/short-and-open-circuits