Absolute pressure: Difference between revisions
J.williams (talk | contribs) m (1 revision imported) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Done | [[Category:Done 2017-07-01]] | ||
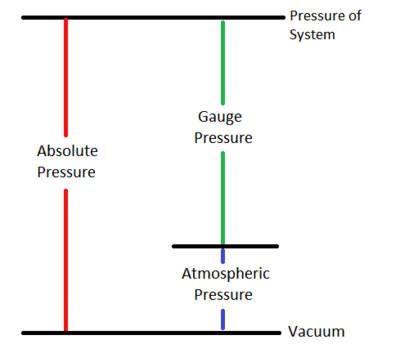
[[File:Pressure.png|400px|thumbnail|right|Figure 1: Possible pressure measurements of a system.]] | |||
<onlyinclude>'''Absolute pressure''' is the measure of [[pressure]] with respect to ''absolute zero pressure'', which is the pressure of a perfect [[vacuum]].</onlyinclude><ref>The Engineering Toolbox. (April 4, 2015). ''Pressure'' [Online]. Available: http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/pressure-d_587.html</ref> The absolute pressure measurement is required for the [[ideal gas law]] in the same sense that [[temperature]] must be represented by its absolute unit, the [[Kelvin]]. | <onlyinclude>'''Absolute pressure''' is the measure of [[pressure]] with respect to ''absolute zero pressure'', which is the pressure of a perfect [[vacuum]].</onlyinclude><ref>The Engineering Toolbox. (April 4, 2015). ''Pressure'' [Online]. Available: http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/pressure-d_587.html</ref> The absolute pressure measurement is required for the [[ideal gas law]] in the same sense that [[temperature]] must be represented by its absolute unit, the [[Kelvin]]. | ||
Many pressure measurements on Earth, like [[tire pressure]] subtract off the pressure from the [[atmosphere]], which is a [[gauge pressure]]. This can confuse matters because this pressure is also measured in the same units. Absolute pressure is given by the gauge pressure plus [[atm|atmospheric pressure]] for measurements on Earth. | Many pressure measurements on Earth, like [[tire pressure]] subtract off the pressure from the [[atmosphere]], which is a [[gauge pressure]]. This can confuse matters because this pressure is also measured in the same units. Absolute pressure is given by the gauge pressure plus [[atm|atmospheric pressure]] for measurements on Earth. | ||
[[ | |||
See also [[gauge pressure]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
[[Category:Uploaded]] | [[Category:Uploaded]] | ||
Revision as of 23:02, 17 August 2017
Absolute pressure is the measure of pressure with respect to absolute zero pressure, which is the pressure of a perfect vacuum.[1] The absolute pressure measurement is required for the ideal gas law in the same sense that temperature must be represented by its absolute unit, the Kelvin.
Many pressure measurements on Earth, like tire pressure subtract off the pressure from the atmosphere, which is a gauge pressure. This can confuse matters because this pressure is also measured in the same units. Absolute pressure is given by the gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure for measurements on Earth.
See also gauge pressure.
References
- ↑ The Engineering Toolbox. (April 4, 2015). Pressure [Online]. Available: http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/pressure-d_587.html