Electric generator: Difference between revisions
m (1 revision imported) |
energy>Jmdonev No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Done | [[Category:Done 2020-02-29]] | ||
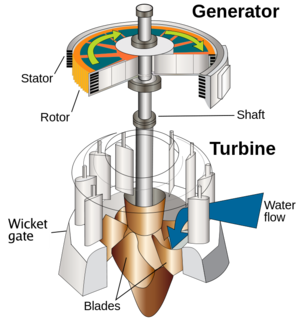
[[File: | [[File:Water_turbine_with_generator.png|thumb|300px|right|Figure 1. Note the water flows in and makes the turbine spin the [[generator]]. The generator then creates [[electricity]] for the [[grid]].<ref>By U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, This file was derived from: Water turbine (en).svg:, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=18581340</ref>]] | ||
<onlyinclude>'''Electric generators''' are used to transform mechanical or [[Kinetic energy|kinetic energy]] into electric [[Potential energy|potential difference]], also known as [[Voltage|voltage]]. </onlyinclude> There are several [[power]] generation applications that require the use of electric generators. The first electric generators created [[direct current]] (DC), but later were replaced with the cheaper, more efficient [[alternating current]]. Almost all power plants use [[AC generation|(AC)]] generators; the exception is [[photovoltaic cell]]s. | <onlyinclude>'''Electric generators''' are used to transform mechanical or [[Kinetic energy|kinetic energy]] into electric [[Potential energy|potential difference]], also known as [[Voltage|voltage]]. </onlyinclude> There are several [[power]] generation applications that require the use of electric generators. The first electric generators created [[direct current]] (DC), but later were replaced with the cheaper, more efficient [[alternating current]]. Almost all power plants use [[AC generation|(AC)]] generators; the exception is [[photovoltaic cell]]s. | ||
Electric generators get their kinetic [[energy]] from a [[fuel]] (like [[natural gas]]) or a [[flow]] (like [[hydropower]] or [[wind]]). One particular kind of generator that runs off of [[diesel]] is the [[diesel generator]]; these are often useful in remote areas like Canada's far North, for the [[Yukon power grid]]. | Electric generators get their kinetic [[energy]] from a [[fuel]] (like [[natural gas]]) or a [[primary energy flow]] (like [[hydropower]] or [[wind]]). One particular kind of generator that runs off of [[diesel]] is the [[diesel generator]]; these are often useful in remote areas like Canada's far North, for the [[Yukon power grid]]. | ||
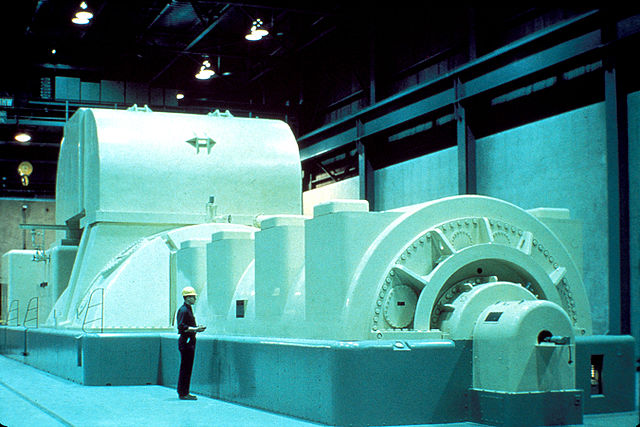
Figure 1 shows how a [[fluid]] would turn a [[shaft]] which in then turns the electric generator. Figure 2 shows an actual electric generator, attached to a turbine. | |||
[[File:steamturbinegen.jpg|thumb|center|700px|Figure 2. An electric generator and turbine.<ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4f/Modern_Steam_Turbine_Generator.jpg</ref>]] | |||
== For Further Reading == | == For Further Reading == | ||
Revision as of 22:01, 10 April 2020
Electric generators are used to transform mechanical or kinetic energy into electric potential difference, also known as voltage. There are several power generation applications that require the use of electric generators. The first electric generators created direct current (DC), but later were replaced with the cheaper, more efficient alternating current. Almost all power plants use (AC) generators; the exception is photovoltaic cells.
Electric generators get their kinetic energy from a fuel (like natural gas) or a primary energy flow (like hydropower or wind). One particular kind of generator that runs off of diesel is the diesel generator; these are often useful in remote areas like Canada's far North, for the Yukon power grid.
Figure 1 shows how a fluid would turn a shaft which in then turns the electric generator. Figure 2 shows an actual electric generator, attached to a turbine.
For Further Reading
For further information please see the related pages below:
References
- ↑ By U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, This file was derived from: Water turbine (en).svg:, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=18581340
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4f/Modern_Steam_Turbine_Generator.jpg

