Venturi effect: Difference between revisions
J.williams (talk | contribs) m (1 revision imported) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Done 2015- | [[Category: Done 2015-09-06]] | ||
[[File:Venturifixed2.PNG|400px|thumb|Figure 1. A diagram demonstrating the Venturi effect. The fluid flows faster in at point 2 than at point 1 due to the decrease in cross-sectional area. The [[pressure]] at point 1 is higher however, due to the [[conservation of energy]].<ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/54/Venturifixed2.PNG</ref>]] | [[File:Venturifixed2.PNG|400px|thumb|Figure 1. A diagram demonstrating the Venturi effect. The fluid flows faster in at point 2 than at point 1 due to the decrease in cross-sectional area. The [[pressure]] at point 1 is higher however, due to the [[conservation of energy]].<ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/54/Venturifixed2.PNG</ref>]] | ||
<onlyinclude>The '''Venturi effect''' describes how the [[velocity]] of the [[fluid]] increases (thus increasing the [[kinetic energy]] of the water) as the cross section of the container decreases, like in a funnel.</onlyinclude> In the case of tidal stream generators a duct or shroud (otherwise known as a diffuser) can be used to increase the amount of power available. A funnel shape is built around or near the [[turbine]] that causes the flow rate of the water to accelerate - sometimes dramatically. These can cause up to 4 or 5 times higher power output than a similar sized turbine without a shroud because it's harnessing the energy from a greater amount of water.<ref name=Ref11>Wise Geek. (August 7, 2015). ''What is a Venturi tube?'' [Online], Available: http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-venturi-tube.htm</ref> | <onlyinclude>The '''Venturi effect''' describes how the [[velocity]] of the [[fluid]] increases (thus increasing the [[kinetic energy]] of the [[water]]) as the cross section of the container decreases, like in a funnel.</onlyinclude> In the case of tidal stream generators a duct or shroud (otherwise known as a diffuser) can be used to increase the amount of [[power]] available. A funnel shape is built around or near the [[turbine]] that causes the [[flow rate]] of the water to accelerate - sometimes dramatically. These can cause up to 4 or 5 times higher power output than a similar sized turbine without a shroud because it's harnessing the [[energy]] from a greater amount of water.<ref name=Ref11>Wise Geek. (August 7, 2015). ''What is a Venturi tube?'' [Online], Available: http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-venturi-tube.htm</ref> | ||
Many different styles of [[tidal stream generator]]s can harness the Venturi effect. | Many different styles of [[tidal stream generator]]s can harness the Venturi effect. | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 3 September 2015
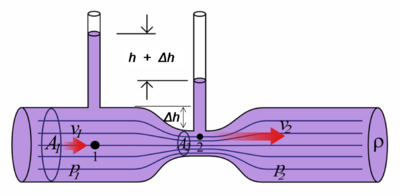
Figure 1. A diagram demonstrating the Venturi effect. The fluid flows faster in at point 2 than at point 1 due to the decrease in cross-sectional area. The pressure at point 1 is higher however, due to the conservation of energy.[1]
The Venturi effect describes how the velocity of the fluid increases (thus increasing the kinetic energy of the water) as the cross section of the container decreases, like in a funnel. In the case of tidal stream generators a duct or shroud (otherwise known as a diffuser) can be used to increase the amount of power available. A funnel shape is built around or near the turbine that causes the flow rate of the water to accelerate - sometimes dramatically. These can cause up to 4 or 5 times higher power output than a similar sized turbine without a shroud because it's harnessing the energy from a greater amount of water.[2]
Many different styles of tidal stream generators can harness the Venturi effect.
References
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/54/Venturifixed2.PNG
- ↑ Wise Geek. (August 7, 2015). What is a Venturi tube? [Online], Available: http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-venturi-tube.htm

