Heptane: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (1 revision imported) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Done | [[Category:Done 2020-01-31]] | ||
[[Category: Translated to French]] | |||
<!--T:1--> | |||
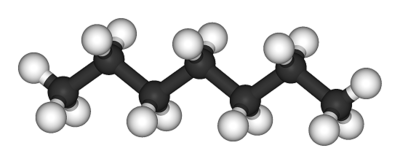
[[File:Heptane-3D-balls.png|thumb|400px|framed|right|Figure 1. Ball and stick model of heptane, the white balls represent [[hydrogen]] atoms and the black balls represent [[carbon]] atoms.<ref>"Heptane-3D-balls". Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Heptane-3D-balls.png#mediaviewer/File:Heptane-3D-balls.png</ref>]] | |||
<!--T:2--> | |||
<onlyinclude>'''Heptane''' is an [[alkane]] with the chemical formula C<sub>7</sub>H<sub>16</sub>. As a [[hydrocarbon]], it can undergo [[hydrocarbon combustion]] which gives off heat energy.</onlyinclude> | |||
Heptane is a [[volatile]], colourless [[liquid]] that is odourless when pure.<ref name=pubchem> National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2015). ''Properties of Heptane'' [Online]. Available: http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/heptane [February 16,2015]. </ref> | |||
Heptane is an important hydrocarbon as it, along with pure [[octane]], sets the extreme ends of the [[octane rating]] scale. Heptane is used to set the standard zero point | <!--T:3--> | ||
Heptane is an important hydrocarbon (or [[organic molecule]] as it, along with pure [[octane]], sets the extreme ends of the [[octane rating]] scale. Heptane is used to set the standard zero point. This means that as a [[fuel]] it burns in a way that is unhelpful within an [[engine]], specifically, it combusts when put under pressure. This is why higher octane ratings are better for an engine. Heptane is a terrible fuel choice for a car since it burns explosively, causing [[octane rating #Pre-Ignition and Knocking|engine knocking]]. As well as setting the zero point for octane rating, heptane is frequently used as a laboratory [[solvent]] due to it's low reactivity with other molecules. Many substances that will not dissolve in [[water]] do dissolve in heptane.<ref> Education Portal. (2015). ''Heptane: Structure, Uses, & Formula'' [Online]. Available: http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/heptane-structure-uses-formula.html [February 16, 2015]</ref> | |||
==Properties== <!--T:4--> | |||
==Properties== | |||
Below is a table of some of the basic properties of heptane. | Below is a table of some of the basic properties of heptane. | ||
<!--T:5--> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 22: | Line 25: | ||
| [[Boiling point]] || 98<sup>o</sup>C<ref name =elmhurst/> | | [[Boiling point]] || 98<sup>o</sup>C<ref name =elmhurst/> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Combustion Reaction== <!--T:6--> | |||
<!--T:7--> | |||
Heptane undergoes [[hydrocarbon combustion]], combining with [[oxygen]] to form [[carbon dioxide]]. The balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of heptane is: | |||
<!--T:8--> | |||
<center>C<sub>7</sub>H<sub>16</sub> + 11O<sub>2</sub> → 7CO<sub>2</sub> + 8H<sub>2</sub>O + Heat Energy ([[Enthalpy]]) </center> | |||
<!--T:9--> | |||
The [[hydrocarbon combustion]] reaction releases [[heat]] [[energy]] and is an example of an [[exothermic reaction]]. The reaction also has a negative [[enthalpy]] change (ΔH) value. | |||
==For Further Reading== | |||
*[[Chemical energy]] | |||
*[[Chemical bond]] | |||
*[[Combustion]] | |||
*[[Primary energy]] | |||
*[[Energy conversion technology]] | |||
*Or explore a [[Special:Random|random page]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
[[Category:Uploaded]] | [[Category:Uploaded]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:02, 27 September 2021
Heptane is an alkane with the chemical formula C7H16. As a hydrocarbon, it can undergo hydrocarbon combustion which gives off heat energy. Heptane is a volatile, colourless liquid that is odourless when pure.[2]
Heptane is an important hydrocarbon (or organic molecule as it, along with pure octane, sets the extreme ends of the octane rating scale. Heptane is used to set the standard zero point. This means that as a fuel it burns in a way that is unhelpful within an engine, specifically, it combusts when put under pressure. This is why higher octane ratings are better for an engine. Heptane is a terrible fuel choice for a car since it burns explosively, causing engine knocking. As well as setting the zero point for octane rating, heptane is frequently used as a laboratory solvent due to it's low reactivity with other molecules. Many substances that will not dissolve in water do dissolve in heptane.[3]
Properties
Below is a table of some of the basic properties of heptane.
| Chemical formula | C7H16 |
| Molar mass | 100.21 grams/mole |
| Melting point | -91oC[4] |
| Boiling point | 98oC[4] |
Combustion Reaction
Heptane undergoes hydrocarbon combustion, combining with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. The balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of heptane is:
The hydrocarbon combustion reaction releases heat energy and is an example of an exothermic reaction. The reaction also has a negative enthalpy change (ΔH) value.
For Further Reading
- Chemical energy
- Chemical bond
- Combustion
- Primary energy
- Energy conversion technology
- Or explore a random page
References
- ↑ "Heptane-3D-balls". Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Heptane-3D-balls.png#mediaviewer/File:Heptane-3D-balls.png
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2015). Properties of Heptane [Online]. Available: http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/heptane [February 16,2015].
- ↑ Education Portal. (2015). Heptane: Structure, Uses, & Formula [Online]. Available: http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/heptane-structure-uses-formula.html [February 16, 2015]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Charles E. Ophardt. (2003). Virtual Chembook - Hydrocarbon Boiling Points [Online]. Available: http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/vchembook/501hcboilingpts.html [February 16,2015].