Nonane: Difference between revisions
J.williams (talk | contribs) m (1 revision imported) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category: Done | [[Category:Done 2017-07-01]] | ||
< | <translate> | ||
<!--T:1--> | |||
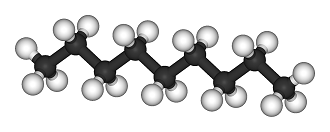
[[File:Nonane-3D-balls.png|200px|framed|right|Figure 1. Ball and stick model of nonane, the white balls represent [[hydrogen]] atoms and the black balls represent [[carbon]] atoms.<ref> "Nonane-3D-balls". Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png#mediaviewer/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png </ref>]] | |||
[[ | <!--T:2--> | ||
<onlyinclude>'''Nonane''' is an [[alkane]] with the [[chemical]] formula C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>20</sub>. | |||
As a [[hydrocarbon]], it can undergo [[hydrocarbon combustion]] and can be burned as a [[fuel]].</onlyinclude> Nonane is a [[volatile]], colourless [[liquid]] that has a gasoline-like odour. Nonane, like other [[alkane]]s, is insoluble in [[water]].<ref name=pubchem> National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2015). ''Properties of Nonane'' [Online]. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/nonane#section=Color [February 16,2015]. </ref> | |||
<!--T:3--> | |||
Normally, nonane is obtained from refining [[petroleum]]. However, it can also be produced by adding hydrogen (H<sub>2</sub>), to [[nonene]] (a closely related [[organic molecule]] with the formula: C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>18</sub>), an [[alkene]]. This reaction is known as [[hydrogenation]]. Nonane is also a component in [[gasoline|automotive]] and [[jet fuel]]. The second major use for nonane is as an ingredient in organic [[solvent]]s. Since nonane is insoluble in water, it makes it a good solvent for other hydrophobic molecules.<ref> Andrea Kropp. (2015). ''Nonane: Structure & Uses'' [Online]. Available: http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/nonane-structure-uses.html [February 16, 2015]. </ref> | |||
==Properties== <!--T:4--> | |||
<!--T:5--> | |||
Below is a table of some of the basic properties of nonane. | Below is a table of some of the basic properties of nonane. | ||
<!--T:6--> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 25: | Line 28: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==References== | ==Combustion Reaction== <!--T:7--> | ||
<!--T:8--> | |||
Nonane undergoes [[hydrocarbon combustion]], combining with [[oxygen]] to form [[carbon dioxide]]. The balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of nonane is: | |||
<!--T:9--> | |||
<center>C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>2</sub><sub>0</sub> + 14O<sub>2</sub> → 9CO<sub>2</sub> + 10H<sub>2</sub>O + Heat Energy ([[Enthalpy]]) </center> | |||
<!--T:10--> | |||
The [[hydrocarbon combustion]] reaction releases [[heat]] [[energy]] and is an example of an [[exothermic reaction]]. The reaction also has a negative [[enthalpy]] change (ΔH) value. | |||
==References== <!--T:11--> | |||
</translate> | |||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
[[Category:Uploaded]] | [[Category:Uploaded]] | ||
<languages /> | |||
Revision as of 17:02, 14 July 2017
<translate>
Nonane is an alkane with the chemical formula C9H20. As a hydrocarbon, it can undergo hydrocarbon combustion and can be burned as a fuel. Nonane is a volatile, colourless liquid that has a gasoline-like odour. Nonane, like other alkanes, is insoluble in water.[2]
Normally, nonane is obtained from refining petroleum. However, it can also be produced by adding hydrogen (H2), to nonene (a closely related organic molecule with the formula: C9H18), an alkene. This reaction is known as hydrogenation. Nonane is also a component in automotive and jet fuel. The second major use for nonane is as an ingredient in organic solvents. Since nonane is insoluble in water, it makes it a good solvent for other hydrophobic molecules.[3]
Properties
Below is a table of some of the basic properties of nonane.
| Chemical formula | C9H20 |
| Molar mass | 128.26 grams/mole |
| Melting point | -51oC[4] |
| Boiling point | 151oC[4] |
Combustion Reaction
Nonane undergoes hydrocarbon combustion, combining with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. The balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of nonane is:
The hydrocarbon combustion reaction releases heat energy and is an example of an exothermic reaction. The reaction also has a negative enthalpy change (ΔH) value.
References
</translate>
- ↑ "Nonane-3D-balls". Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png#mediaviewer/File:Nonane-3D-balls.png
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2015). Properties of Nonane [Online]. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/nonane#section=Color [February 16,2015].
- ↑ Andrea Kropp. (2015). Nonane: Structure & Uses [Online]. Available: http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/nonane-structure-uses.html [February 16, 2015].
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Charles E. Ophardt. (2003). Virtual Chembook - Hydrocarbon Boiling Points [Online]. Available: http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/vchembook/501hcboilingpts.html [February 16,2015].
<languages />