Climate change: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[category:371 topics]] | [[category:371 topics]] | ||
[[Category:Done 2018-12-10]] | [[Category:Done 2018-12-10]] | ||
<onlyinclude>[[Greenhouse gas]]es (GHG's) that come from the [[combustion]] of [[fossil fuel]]s are changing the Earth's [[climate]].<ref name = oxford>Jelley., Dictionary of Energy Science: Oxford University Press</ref> The world is [[global warming|warming]], and there are many different phenomena that [[climate forcing|force the Earth's climate]] to become hotter or colder. While some of these are [[anthropogenic]] and some are [[Natural vs anthropogenic climate change|natural]] (see [[Natural vs anthropogenic climate change|here for a discussion of the difference), [[carbon dioxide]] released from pursuing [[energy service]]s is by far the largest contributor to the planet's current changes in climate.</onlyinclude><ref name = IPCC/> | <onlyinclude>[[Greenhouse gas]]es (GHG's) that come from the [[combustion]] of [[fossil fuel]]s are changing the Earth's [[climate]].<ref name = oxford>Jelley., Dictionary of Energy Science: Oxford University Press</ref> The world is [[global warming|warming]], and there are many different phenomena that [[climate forcing|force the Earth's climate]] to become hotter or colder. While some of these are [[anthropogenic]] and some are [[Natural vs anthropogenic climate change|natural]] (see [[Natural vs anthropogenic climate change|here]] for a discussion of the difference), [[carbon dioxide]] released from pursuing [[energy service]]s is by far the largest contributor to the planet's current changes in climate.</onlyinclude><ref name = IPCC/> | ||
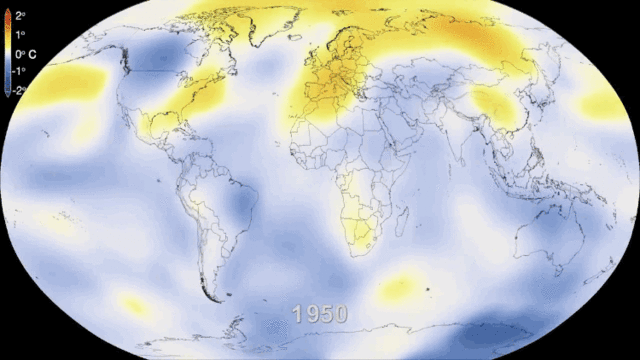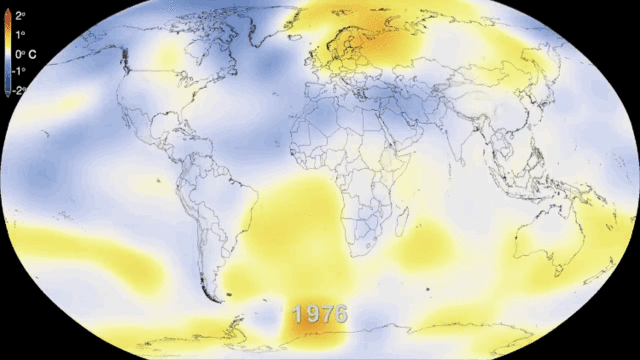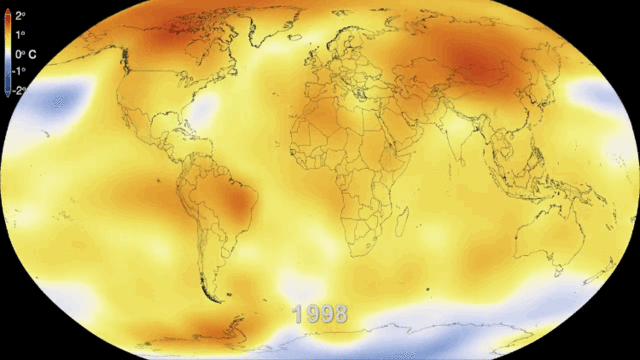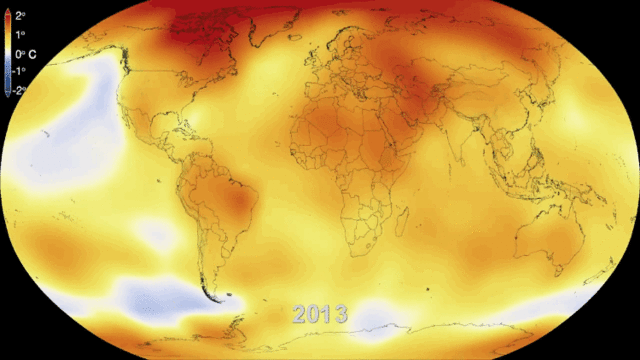
[[File:climate-change-33.gif|900px|thumb|center|Figure 1. Sixty years of global warming.<ref>While these data are from NASA, this image was downloaded from http://bgr.com/2014/01/29/global-warming-gif-video/ on September 4th, 2015.</ref>]] | [[File:climate-change-33.gif|900px|thumb|center|Figure 1. Sixty years of global warming.<ref>While these data are from NASA, this image was downloaded from http://bgr.com/2014/01/29/global-warming-gif-video/ on September 4th, 2015.</ref>]] | ||
Revision as of 05:05, 25 February 2019
Greenhouse gases (GHG's) that come from the combustion of fossil fuels are changing the Earth's climate.[1] The world is warming, and there are many different phenomena that force the Earth's climate to become hotter or colder. While some of these are anthropogenic and some are natural (see here for a discussion of the difference), carbon dioxide released from pursuing energy services is by far the largest contributor to the planet's current changes in climate.[2]
There is no magic temperature that the Earth should be at, but the climate is changing rapidly and this causes problems for all living things, including people. Some of the troubling aspects of climate change include:
- An overall warming of the planet, referred to as global warming (a part of climate change).
- A change in ocean chemistry called ocean acidification, that could lead to a major die-out of ocean life (which many people rely on for food).
- An increase in extreme weather events, like heat waves and very strong hurricanes.
- Increased severity of floods and droughts because of changing precipitation patterns.
There are various signs indicating that climate change is already happening, and will continue to happen. In the IPCC's 2018 special report, it stated on average the Earth's temperature raises by 0.2°C every decade.[2] From pre-industrial levels, the special report states the Earth's average temperature has already been raised by approximately 1.0°C. The special report outlines how irreversible and unprecedented damage will occur when the earth's average temperature raises by 1.5°C from pre-industrial times. If you are interested in checking out the full report, click here
GHG's mix in the atmosphere and travel around the world. This means that it is a global issue which will effect everyone, regardless if they are the source that emitted the GHG's or not. In contrast, something like air pollution, is more localized.
Humans use energy to maintain a high energy society that provides a good quality of life. This means the amount of energy that people use keeps increasing (see the pages on the BRIC and N11 countries for great examples of this). Unfortunately, most of the world's primary energy comes from fossil fuels, which is why climate change is so hard to stop.
There are lots of fossil fuels left. In fact, the biggest problem the world is facing isn't that fossil fuels are going to run out! We have enough to continue burning these fuels for decades to come. However, it will continue to induce problematic global warming, and climate change in general.
Governments will need to intervene to slow down the effects of climate change, however, individuals also make choices on their daily energy consumption as well. In the future, how climate change will effect the globe will depend on how much fossil fuels are burnt, and at what rate they are burning.
The more humans burn fossil fuels, and let carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, the more climate change will hurt people.
For Further Reading
- High energy society
- Climate forcing
- Indicators of a warming world
- Renewable and sustainable energy
- Or explore a random page
References
- ↑ Jelley., Dictionary of Energy Science: Oxford University Press
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 2018 Special Report. 2018.
- ↑ While these data are from NASA, this image was downloaded from http://bgr.com/2014/01/29/global-warming-gif-video/ on September 4th, 2015.

