Water: Difference between revisions
J.williams (talk | contribs) m (1 revision imported) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Done | [[Category:Done 2018-06-15]] | ||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:1--> | |||
[[File:global-water-volume-fresh-large.jpg|360px|thumb|right|Figure 1. An image of the the total amount of water in the world. The large bubble is all of the water (mostly saltwater) the second bubble is all of the fresh water and the little tiny bubble just south of that is water in lakes and rivers.<ref>USGS . (August 2nd, 2015). ''How much water is there in the world.'' [Online]. Available: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/earthhowmuch.html</ref>]] | [[File:global-water-volume-fresh-large.jpg|360px|thumb|right|Figure 1. An image of the the total amount of water in the world. The large bubble is all of the water (mostly saltwater) the second bubble is all of the fresh water and the little tiny bubble just south of that is water in lakes and rivers.<ref>USGS . (August 2nd, 2015). ''How much water is there in the world.'' [Online]. Available: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/earthhowmuch.html</ref>]] | ||
<onlyinclude>'''Water''' is a [[molecule]] made of one [[oxygen]] and two [[hydrogen]] [[atom]]s. Water is the most important [[chemical]] for life on Earth.</onlyinclude> Water makes up a large portion of every living being therefore every living creature needs water. This is why water is important for [[irrigation]] of [[crop]]s | <!--T:2--> | ||
<onlyinclude>'''Water''' is a [[molecule]] made of one [[oxygen]] and two [[hydrogen]] [[atom]]s. Water is the most important [[chemical]] for life on Earth.</onlyinclude> Water makes up a large portion of every living being therefore every living creature needs water. This is why water is important for [[irrigation]] of [[crop]]s, the health of [[livestock]], as well as direct human consumption (drinking, washing, etc.). Water is also an important part of the conversion of [[primary energy]] into [[energy service]]s (please see [[water use in energy systems]]). | |||
As seen in Figure 1, there's a large amount of water on Earth, but most of it is [[saline]] | <!--T:3--> | ||
As seen in Figure 1, there's a large amount of water on Earth, but most of it is [[saline]]—commonly known as salt water. This water is not suitable for drinking, thus it is not consumed by humans. Most of the [[fresh water]] needed for life is locked up in the [[cryosphere]] ([[glacier]]s and permanent [[snow pack]]s), while the majority of available fresh water is stored in [[groundwater]]. The smallest of the three bubbles on the picture is the surface water; the water that humans can directly access at the Earth's surface. Since there are such small amounts of this consumable water available, water [[pollution]] is a concern. In some parts of the world, the lack of access to clean, fresh water is a serious issue. | |||
==Characteristics== | ==Characteristics== <!--T:4--> | ||
[[File:watermol.png|200px|thumb|Figure 2. Water molecule, made up of two hydrogen and one oxygen atom.<Ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Water_molecule_3D.svg</ref>]] | [[File:watermol.png|200px|thumb|Figure 2. Water molecule, made up of two hydrogen and one oxygen atom.<Ref>Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Water_molecule_3D.svg</ref>]] | ||
The water molecule is one of the lightest molecules that exist (although there are several that are lighter), | The water molecule is one of the lightest molecules that exist (although there are several that are lighter), and it's certainly the lightest molecule that forms a [[liquid]] on Earth. Water forms a liquid at room [[temperature]] because it has such a strong [[electric dipole]]. Water has just about the strongest dipole moment of any molecule because of it's small size. This dipole nature means that the hydrogen in the water is strongly attracted to [[electron]]s around the oxygen, called [[hydrogen bonding]]. This hydrogen bonding of water is not just what makes water a liquid—but what makes it a powerful [[solvent]] through these electric interactions. This allows many important [[chemical reaction]]s to occur in water. | ||
Water exists in three phases on earth, liquid water which is the most abundant, [[solid]] water | <!--T:5--> | ||
Water exists in three phases on earth, liquid water which is the most abundant, [[solid]] water (referred to as [[ice]]) and [[water vapour]] which is the [[gas]]eous form. | |||
==Water and the Climate== | ==Water and the Climate== <!--T:6--> | ||
Water has a huge effect on Earth's [[climate]] and is a major factor in [[weather]] as well (see [[climate vs weather]] for the difference). Weather often includes [[precipitation]] like [[rain]], [[snow]], and [[hail]]. [[Cloud]]s are made largely of small water droplets or frozen crystals. Water vapour is the [[greenhouse gas]] with the biggest effect on the [[temperature of the Earth]], and it has an amplifying effect on the [[global warming]] from [[carbon dioxide]] | Water has a huge effect on Earth's [[climate]] and is a major factor in [[weather]] as well (see [[climate vs weather]] for the difference). Weather often includes [[precipitation]] like [[rain]], [[snow]], and [[hail]]. [[Cloud]]s are made largely of small water droplets or frozen crystals. Water vapour is also the [[greenhouse gas]] with the biggest effect on the [[temperature of the Earth]], and it has an amplifying effect on the [[global warming]] from [[carbon dioxide]]. In other words, water vapour itself doesn't drive climate change, however, amplifies the effects since more CO2 means more water vapour will be in the atmosphere. | ||
Too little water causes [[drought]]s, which are a problem. Too much causes [[flood]]ing, which is also a problem. One of the biggest concerns about [[climate change]] is that it will affect how much water will be in different parts of the world. This has been summed up as "the wet will get wetter and the dry will get drier". Please see [[climate change impacts on water]] for more details. Completely separate from [[climate change]], there's quite a bit of concern about [[water pollution]] | <!--T:7--> | ||
Too little water causes [[drought]]s, which are a problem. Too much causes [[flood]]ing, which is also a problem. One of the biggest concerns about [[climate change]] is that it will affect how much water will be in different parts of the world. This has been summed up as "the wet will get wetter and the dry will get drier". Please see [[climate change impacts on water]] for more details. Completely separate from [[climate change]], there's quite a bit of concern about [[water pollution]] from things like [[acid rain]]. | |||
Water moves through various systems on the planet taking different forms and being transported by different methods including [[evaporation]], [[condensation]], [[melting point|melting]], [[freezing]], [[sublimation]] and just plain water flowing. This motion of water throughout the planet is referred to as the [[hydrologic cycle]]. | Water moves through various systems on the planet taking different forms and being transported by different methods including [[evaporation]], [[condensation]], [[melting point|melting]], [[freezing]], [[sublimation]] and just plain water flowing. This motion of water throughout the planet is referred to as the [[hydrologic cycle]]. | ||
==Fun facts== | ==Fun facts== <!--T:8--> | ||
*Water makes up three quarters of the surface of the Earth. | *Water makes up three quarters of the surface of the Earth. | ||
*Water makes up 60-78% of the [[mass]] of humans (depending on age, babies are more water than adults)<ref>USGS the water school (August 2nd, 2015). ''The water in you'' available: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/propertyyou.html</ref> | *Water makes up 60-78% of the [[mass]] of humans (depending on age, babies are more water than adults)<ref>USGS the water school (August 2nd, 2015). ''The water in you'' available: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/propertyyou.html</ref> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 33: | ||
*Water often transports [[heat]] from deep underground for [[geothermal energy]]. | *Water often transports [[heat]] from deep underground for [[geothermal energy]]. | ||
<!--T:9--> | |||
To learn more about water please see the [http://water.usgs.gov/edu/earthwherewater.html USGS's water page]. | To learn more about water please see the [http://water.usgs.gov/edu/earthwherewater.html USGS's water page]. | ||
==References== | ==For Further Reading== | ||
{{reflist}}[[Category:Uploaded]] | *[[Hydrologic cycle]] | ||
*[[Hydrogen bond]] | |||
*[[Energy from water]] | |||
*[[Power plant]] | |||
*[[Hydroelectricity]] | |||
*[[Life cycle]] | |||
*Or explore a [[Special:Random|random page]] | |||
==References== <!--T:10--> | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
</translate> | |||
<languages /> | |||
[[Category:Uploaded]] | |||
Revision as of 19:34, 6 June 2018
<translate>
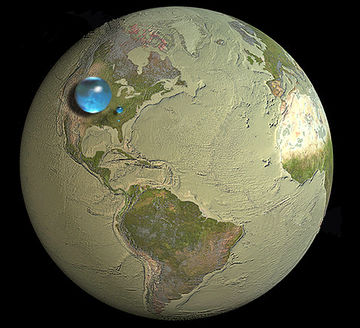
Water is a molecule made of one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms. Water is the most important chemical for life on Earth. Water makes up a large portion of every living being therefore every living creature needs water. This is why water is important for irrigation of crops, the health of livestock, as well as direct human consumption (drinking, washing, etc.). Water is also an important part of the conversion of primary energy into energy services (please see water use in energy systems).
As seen in Figure 1, there's a large amount of water on Earth, but most of it is saline—commonly known as salt water. This water is not suitable for drinking, thus it is not consumed by humans. Most of the fresh water needed for life is locked up in the cryosphere (glaciers and permanent snow packs), while the majority of available fresh water is stored in groundwater. The smallest of the three bubbles on the picture is the surface water; the water that humans can directly access at the Earth's surface. Since there are such small amounts of this consumable water available, water pollution is a concern. In some parts of the world, the lack of access to clean, fresh water is a serious issue.
Characteristics
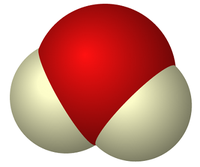
The water molecule is one of the lightest molecules that exist (although there are several that are lighter), and it's certainly the lightest molecule that forms a liquid on Earth. Water forms a liquid at room temperature because it has such a strong electric dipole. Water has just about the strongest dipole moment of any molecule because of it's small size. This dipole nature means that the hydrogen in the water is strongly attracted to electrons around the oxygen, called hydrogen bonding. This hydrogen bonding of water is not just what makes water a liquid—but what makes it a powerful solvent through these electric interactions. This allows many important chemical reactions to occur in water.
Water exists in three phases on earth, liquid water which is the most abundant, solid water (referred to as ice) and water vapour which is the gaseous form.
Water and the Climate
Water has a huge effect on Earth's climate and is a major factor in weather as well (see climate vs weather for the difference). Weather often includes precipitation like rain, snow, and hail. Clouds are made largely of small water droplets or frozen crystals. Water vapour is also the greenhouse gas with the biggest effect on the temperature of the Earth, and it has an amplifying effect on the global warming from carbon dioxide. In other words, water vapour itself doesn't drive climate change, however, amplifies the effects since more CO2 means more water vapour will be in the atmosphere.
Too little water causes droughts, which are a problem. Too much causes flooding, which is also a problem. One of the biggest concerns about climate change is that it will affect how much water will be in different parts of the world. This has been summed up as "the wet will get wetter and the dry will get drier". Please see climate change impacts on water for more details. Completely separate from climate change, there's quite a bit of concern about water pollution from things like acid rain.
Water moves through various systems on the planet taking different forms and being transported by different methods including evaporation, condensation, melting, freezing, sublimation and just plain water flowing. This motion of water throughout the planet is referred to as the hydrologic cycle.
Fun facts
- Water makes up three quarters of the surface of the Earth.
- Water makes up 60-78% of the mass of humans (depending on age, babies are more water than adults)[3]
- Water is a byproduct of combustion, usually in the form of water vapour.
- Water is used to turn the heat into work in coal-fired power plants, natural gas power plants and nuclear power plants.
- Water is also often used as the cold sink in the same power plants by dumping the waste heat into rivers, lakes or the ocean.
- Water often transports heat from deep underground for geothermal energy.
To learn more about water please see the USGS's water page.
For Further Reading
- Hydrologic cycle
- Hydrogen bond
- Energy from water
- Power plant
- Hydroelectricity
- Life cycle
- Or explore a random page
References
- ↑ USGS . (August 2nd, 2015). How much water is there in the world. [Online]. Available: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/earthhowmuch.html
- ↑ Wikimedia Commons [Online], Available: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Water_molecule_3D.svg
- ↑ USGS the water school (August 2nd, 2015). The water in you available: http://water.usgs.gov/edu/propertyyou.html
</translate> <languages />

